The Silent Struggle: Bulimia’s Devastating Impact on Women’s Dental Health
Introduction:
Bulimia nervosa, a serious eating disorder characterized by binge-eating followed by purging behaviors, affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is five times more prevalent in women than in men. While the detrimental effects on mental and physical health are well-documented, the impact on oral health, specifically women’s teeth, remains a silent and often overlooked consequence.
The Prevalence of Bulimia and its relation to Dental Health:
Statistics reveal that between 2.4% and 4% of women will experience some degree of bulimia during their lifetime. The act of purging through vomiting exposes teeth to stomach acids, leading to the erosion of the protective outer enamel layer of teeth. Once enamel is compromised, teeth become more susceptible to decay, setting the stage for a cascade of dental issues.
The role of stomach acids and decreased salivary flow:
The acids from the stomach during purging dissolve tooth enamel and exacerbate existing dental damage. Furthermore, most women with bulimia experience reduced salivary flow, a crucial component in protecting teeth from aggressive bacteria that contribute to tooth decay. Additionally, common medications used for psychological treatments, such as anti-depressants, further decrease salivary flow, compounding the risk of dental deterioration caused by stomach acid erosion.
Sugar cravings and their Impact:
A well-known aspect of bulimia is the tendency to crave carbonated beverages or sweet, sugary foods after purging. The high sugar content in these choices encourages aggressive bacterial growth, accelerating tooth decay and complicating the oral health challenges associated with bulimia.
Symptoms and Consequences:
Dental symptoms associated with bulimia include sensitivity to hot and cold, difficulty chewing, and visually changed worn-down teeth with smooth or glassy surfaces. The negative appearance of damaged teeth plays a significant role in the self-esteem of individuals with bulimia, contributing to feelings of embarrassment and shame.
Treatment Options for Dental Rehabilitation:
Addressing the dental consequences of bulimia requires a multi-faceted approach. At the top of the list is a caring, dental healthcare professional, who truly understands the nature of bulimia nervosa and its effects on the psychological well-being and self-esteem of the patient. Compassion and empathy are extremely important to establish trust in the doctor patient relationship.
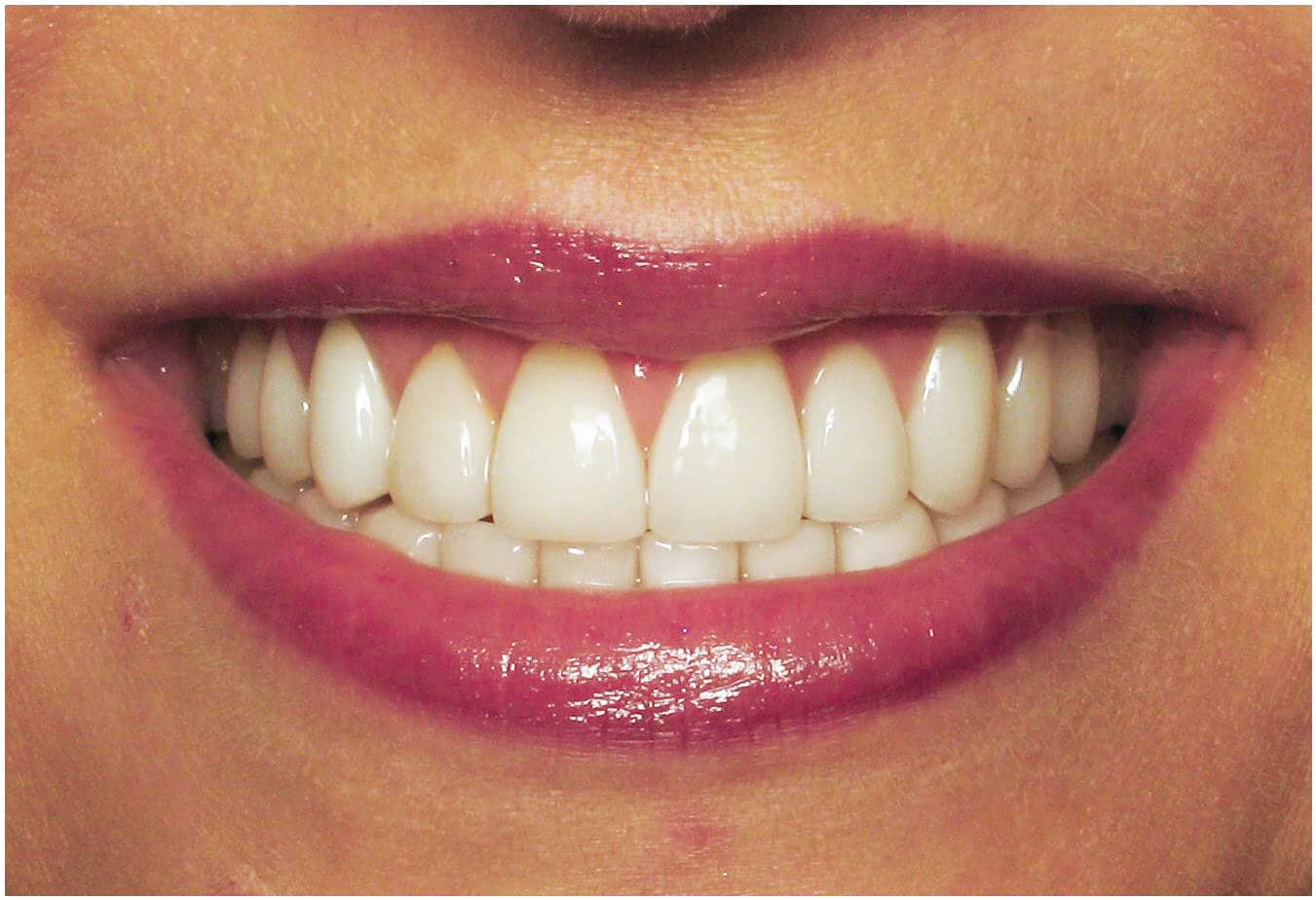
Fluoride application to strengthen tooth surfaces and porcelain veneers to repair teeth are the most common initial dental treatments. Porcelain veneers are thin pieces of porcelain covering teeth that can restore or enhance the original look of teeth. They also protect eroded tooth surfaces from further damage. When tooth damage is severe porcelain crowns may also be necessary to reestablish a normal bite and improve the overall cosmetic appearance of the mouth.
The Psychological Toll and Reluctance to Smile:
Women with bulimia often avoid smiling due to the fear of revealing their dental damage. The wear on tooth surfaces becomes a source of embarrassment, perpetuating the cycle of avoidance. Dental professionals play a crucial role in not only restoring oral health but also addressing in a positive way the psychological impact of the disorder.
Conclusion:
Bulimia’s damaging effects on women’s teeth extend beyond the physical realm, impacting self-esteem and overall well-being. Early intervention and comprehensive dental care are essential components in breaking the cycle of oral health decline associated with this complex and challenging disorder. Seeking support from truly caring and empathetic dental professionals as well as mental health experts can pave the way for recovery and a healthier, more confident smile.